
#Atomic number c full
These are either typedefs of the corresponding full specialization of the atomic class template or a base class of such specialization.Ītomics for width-based integrals (those defined in ).Įach of these is either an alias of one of the above atomics for fundamental integral types or of a full specialization of the atomic class template with an extended integral type. The following atomic types are also defined in this header each with the same behavior as the respective instantiation of atomic for the listed contained type. The header also declares an entire set of C-style types and functions compatible with the atomic support in C.Ĭlasses atomic Atomic (class template) atomic_flag Atomic flag (class) This header declares two C++ classes, atomic and atomic_flag, that implement all the features of atomic types in self-contained classes. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.Atomic types are types that encapsulate a value whose access is guaranteed to not cause data races and can be used to synchronize memory accesses among different threads. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. See also: Atomic Number – Does it conserve in a nuclear reaction? Atomic Number and Chemical PropertiesĮvery solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus.

The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs.
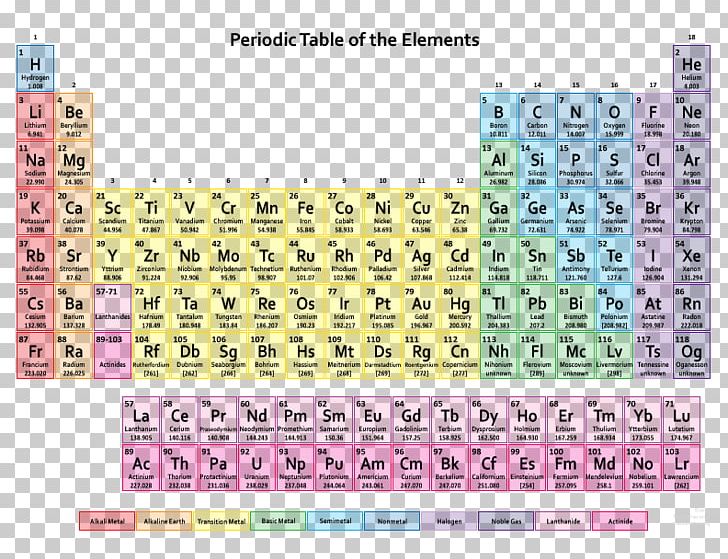
Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons.

The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
